Learn about the concept of smart cities and their role in urban development. Discover how smart cities use technology and data to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and livability. Explore the benefits and challenges of implementing smart city initiatives. Find out how cities like Tokyo, Dubai, Amsterdam, and Songdo are leading the way in embracing smart technologies. Understand the importance of privacy, security, bridging the digital divide, and ethical considerations in smart city development.
Exploring the Concept and Role of Smart Cities in Urban Development
Introduction
In recent years, the concept of smart cities has gained significant attention in the field of urban development. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, cities around the world are embracing the idea of becoming “smart” to improve the quality of life for their residents. Housing urban development plays a pivotal role in shaping the quality of life for city dwellers. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of smart cities and their role in urban development.
Smart cities are urban areas that leverage technology and data to enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and livability of their communities. These cities utilize various technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics to gather and analyze vast amounts of information. By doing so, they are able to make informed decisions and provide better services to their residents.
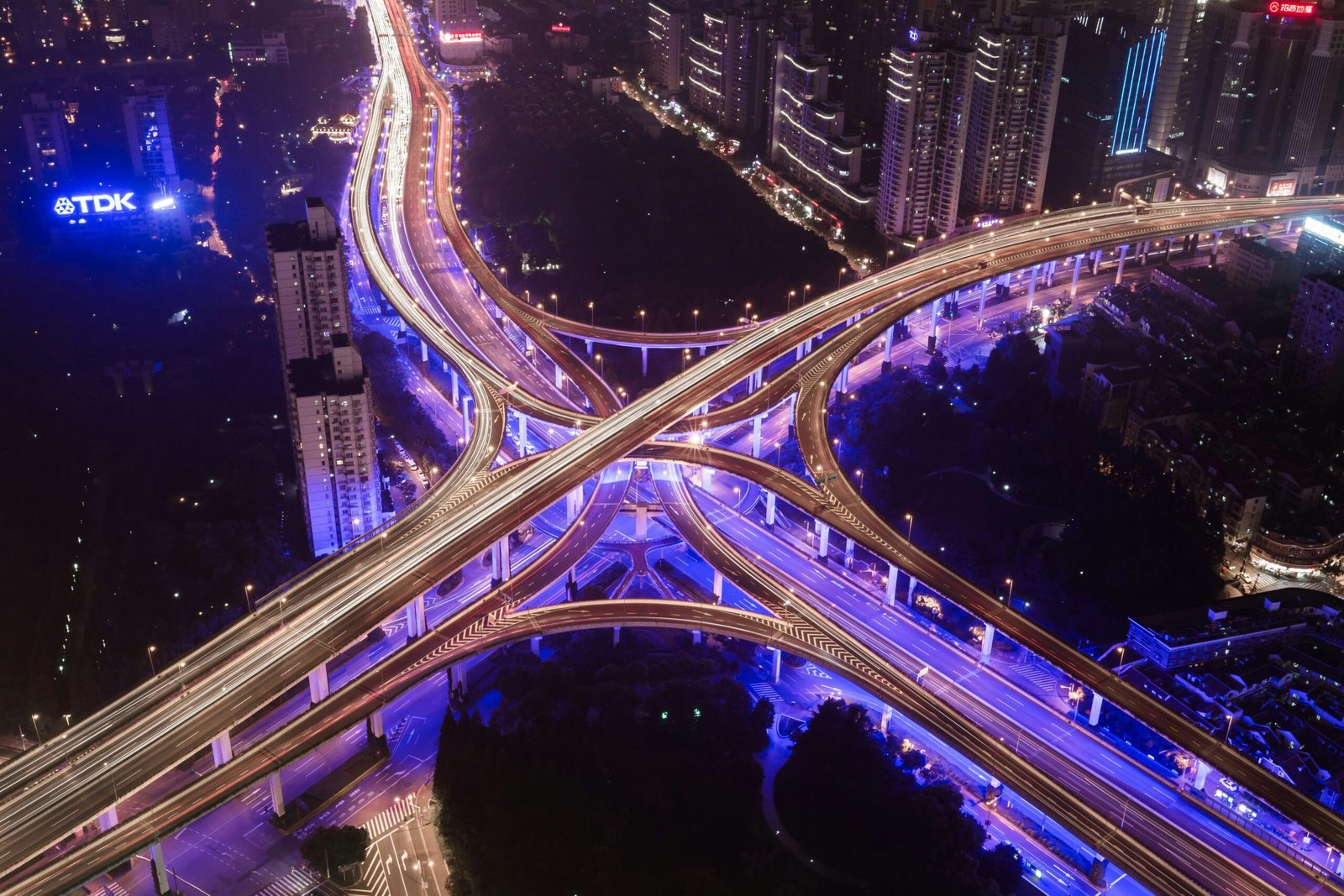
The main goal of a smart city is to create an environment that is interconnected, responsive, and sustainable. By integrating technology into various aspects of urban life, these cities aim to improve the efficiency of transportation systems, enhance public safety, optimize energy consumption, and promote environmental sustainability.
One of the key areas where smart cities have made significant progress is in transportation. Through the use of sensors, cameras, and real-time data analysis, these cities are able to monitor traffic flow, identify congestion points, and optimize transportation routes. This not only reduces travel time for residents but also minimizes fuel consumption and emissions, leading to a greener and more sustainable urban environment.
Another important aspect of smart cities is the concept of smart buildings. These buildings are equipped with advanced sensors and automation systems that enable efficient energy management, waste reduction, and improved occupant comfort. For example, smart buildings can automatically adjust lighting and temperature based on occupancy levels, resulting in significant energy savings. They can also monitor and manage water usage, detect leaks, and optimize waste management processes, leading to a more sustainable use of resources.
Furthermore, smart cities are also focused on improving public safety and security. Through the use of surveillance cameras, facial recognition technology, and data analytics, these cities are able to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. This allows for quicker emergency response times and better overall safety for residents.
In conclusion, the concept of smart cities is revolutionizing urban development by harnessing the power of technology and data. These cities are leveraging advanced technologies to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable environments for their residents. From transportation to energy management to public safety, smart cities are transforming the way we live, work, and interact within urban spaces.
Smart cities are revolutionizing urban living by harnessing the power of technology and data. With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics, cities are transforming into interconnected hubs of innovation and efficiency. By leveraging these digital technologies, smart cities are able to optimize various aspects of urban life, from transportation and energy management to waste disposal and public services.
One of the key features of a smart city is the use of interconnected devices and sensors. These devices are embedded in various infrastructures and collect real-time data on a wide range of parameters. For example, sensors in transportation systems can monitor traffic flow, detect congestion, and provide real-time updates to commuters. Similarly, sensors in energy grids can monitor power consumption, identify areas of inefficiency, and optimize energy distribution.
The data collected by these sensors is then analyzed using advanced analytics techniques. Big data analytics algorithms can process vast amounts of data and extract valuable insights that can be used to improve urban services. For instance, by analyzing transportation data, cities can identify bottlenecks in the road network and optimize traffic flow. By analyzing energy consumption patterns, cities can identify opportunities for energy conservation and implement targeted strategies to reduce carbon emissions.
Furthermore, smart cities also rely on the power of artificial intelligence to automate and streamline urban services. AI algorithms can analyze data in real-time, detect patterns, and make autonomous decisions. For example, AI-powered waste management systems can optimize garbage collection routes based on real-time data, reducing costs and improving efficiency. AI-powered public safety systems can analyze surveillance footage, detect anomalies, and alert authorities in case of emergencies.
In addition to improving efficiency and effectiveness, smart cities also prioritize the well-being and quality of life of their citizens. For instance, smart cities often use technology to enhance public safety. Smart surveillance systems can monitor public spaces, identify potential threats, and provide real-time alerts to law enforcement agencies. Similarly, smart healthcare systems can use wearable devices and remote monitoring technologies to provide personalized healthcare services to citizens.
Overall, smart cities are transforming urban landscapes by harnessing the power of technology and data. By creating interconnected systems and leveraging advanced analytics and AI, these cities are able to enhance the quality of life for their citizens, improve sustainability, and streamline urban services. As technology continues to advance, the potential for smart cities to revolutionize urban living is limitless.
The Role of Smart Cities in Urban Development
Smart cities play a crucial role in urban development by addressing some of the key challenges faced by modern cities. Here are some of the ways in which explore the concept of smart cities and their role in urban development:
1. Improved Infrastructure
Smart cities use technology to improve the infrastructure of a city. For example, sensors embedded in roads can monitor traffic flow and adjust traffic signals in real-time, reducing congestion and improving the overall efficiency of transportation systems. Similarly, smart grids can optimize energy distribution, reducing waste and promoting sustainability. The integration of smart infrastructure not only enhances the quality of life for residents but also attracts businesses and investors, leading to economic growth and development.
2. Enhanced Public Services
Smart cities leverage technology to enhance public services, making them more efficient and accessible. For instance, smart parking systems can guide drivers to available parking spaces, reducing the time spent searching for parking and minimizing traffic congestion. Smart healthcare systems can enable remote monitoring of patients, improving access to healthcare services and reducing the burden on hospitals. Additionally, smart cities can implement intelligent waste management systems that optimize collection routes and reduce environmental impact.
3. Sustainable Development
Smart cities prioritize sustainability and environmental conservation. By using technology to optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and promote renewable energy sources, smart cities contribute to a more sustainable future. For example, smart buildings can automatically adjust lighting and temperature based on occupancy, saving energy and reducing carbon emissions. Furthermore, smart cities can implement smart water management systems that monitor and conserve water resources, ensuring long-term sustainability.
4. Citizen Engagement and Participation
Smart cities empower citizens by providing them with access to real-time information and involving them in decision-making processes. Through mobile applications and online platforms, citizens can report issues, provide feedback, and participate in community initiatives. This fosters a sense of ownership and collaboration, leading to more inclusive and vibrant communities. Moreover, smart cities can utilize data analytics to gather insights into citizen needs and preferences, enabling targeted and effective urban planning.
5. Economic Growth and Innovation
Smart cities stimulate economic growth and innovation by attracting businesses and entrepreneurs. The availability of advanced infrastructure, digital connectivity, and a skilled workforce create an environment conducive to innovation and entrepreneurship. Smart cities also promote the development of technology startups and encourage collaboration between academia, government, and industry. By fostering a culture of innovation and providing opportunities for business growth, smart cities contribute to job creation, economic diversification, and overall prosperity.
In conclusion, smart cities play a multifaceted role in urban development. Through improved infrastructure, enhanced public services, sustainable practices, citizen engagement, and economic growth, smart cities create a foundation for thriving and resilient urban communities. As technology continues to advance, the potential for smart cities to drive positive change and shape the future of urban development is limitless.
Tokyo
Tokyo, the capital of Japan, is also at the forefront of smart city initiatives. The city has implemented various technologies to improve transportation, energy efficiency, and disaster management. Tokyo’s smart city initiatives aim to create a safer and more resilient city for its residents.
Dubai
Dubai, in the United Arab Emirates, is known for its ambitious smart city projects. The city has implemented technologies such as smart grids, autonomous transportation, and digital government services. Dubai’s smart city initiatives aim to create a seamless and efficient experience for residents and visitors.
Amsterdam
Amsterdam, the capital of the Netherlands, is recognized as one of the most innovative and sustainable cities in the world. The city has implemented smart solutions in areas such as energy, mobility, and waste management. Amsterdam’s smart city initiatives focus on creating a city that is not only technologically advanced but also environmentally friendly.
Songdo
Songdo, located in South Korea, is a city that was built from scratch with smart technologies in mind. The city incorporates advanced technologies in areas such as transportation, energy, and waste management. Songdo’s smart city approach aims to create a sustainable and efficient urban environment.
These are just a few examples of cities that are leading the way in embracing smart technologies. The implementation of smart city initiatives is a global trend, with cities around the world recognizing the potential of technology to improve the quality of life for their residents. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see more cities joining the smart city movement and reaping the benefits of a connected and sustainable urban environment.
Challenges and Considerations
While the concept of smart cities holds great promise, there are several challenges and considerations that need to be addressed:
1. Privacy and Security
As smart cities collect and analyze vast amounts of data, privacy and security become major concerns. It is essential to establish robust data protection measures and ensure that citizens’ personal information safeguarded. Additionally, smart city infrastructure must be resilient against cyber threats to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
One specific challenge in ensuring privacy and security is the need for strong encryption protocols. With the increasing volume of data being transmitted and stored in smart city systems, it is crucial to implement encryption techniques that can effectively protect sensitive information from being intercepted or accessed by unauthorized individuals. This requires continuous research and development in the field of cybersecurity to stay ahead of emerging threats.
2. Digital Divide
One of the challenges of implementing smart city initiatives is ensuring that all citizens have access to technology and digital services. The digital divide, which refers to the gap between those who have access to technology and those who do not, needs to addressed to ensure that the benefits of smart cities are inclusive and accessible to all.
To bridge the digital divide, governments and city planners need to prioritize the development of affordable and reliable internet infrastructure. This includes expanding broadband coverage to underserved areas and implementing initiatives to provide low-income households with access to affordable internet services. In addition, efforts should made to provide digital literacy training and support to individuals who may be unfamiliar with technology, ensuring that everyone can fully participate in and benefit from the smart city ecosystem.
3. Cost and Funding
Implementing smart city initiatives can be costly, requiring significant investments in infrastructure, technology, and skilled human resources. Finding sustainable funding models and securing public-private partnerships are essential to ensure the long-term viability of smart city projects.
To address the cost and funding challenges, cities can explore various options. One approach is to seek funding from national and international organizations that support smart city development. Governments can also leverage public-private partnerships, where private companies invest in smart city projects in exchange for long-term revenue streams. Additionally, cities can explore innovative financing models, such as green bonds or impact investments, to attract capital for sustainable and resilient infrastructure development.
4. Ethical Considerations
As smart city technologies become more advanced, ethical considerations need to taken into account. For example, the use of surveillance technologies for public safety purposes must balanced with the protection of individual privacy rights. It is crucial to establish ethical guidelines and ensure that smart city initiatives implemented in a way that respects individual rights and freedoms.
In addition to privacy concerns, there are other ethical considerations that need to addressed. For instance, the deployment of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in smart city systems should be transparent and accountable, ensuring that decisions made by these algorithms are fair and unbiased. Furthermore, there should be mechanisms in place to address potential biases or discrimination that may arise from the use of AI in areas such as transportation, healthcare, and law enforcement.
Overall, while the potential benefits of smart cities are vast, it is crucial to address the challenges and considerations associated with their implementation. By prioritizing privacy and security, bridging the digital divide, finding sustainable funding models, and considering ethical implications, cities can create smart city ecosystems that are inclusive, resilient, and beneficial for all citizens.









2 Comments